
Malaria
Malaria is a parasitic disease causing 241 million clinical infections and 627,000 deaths annually in endemic countries1, and is a constant threat to travelers from other countries who lack any immunity to malaria. Despite a supply of artemisinin combination therapies and bed nets to treat malaria and prevent transmission, and a partially effective vaccine in the periphery, these tools alone are unlikely to allow regional malaria elimination in the near future.
Drugs in the travel medicine market have been only partially adequate and have typically not protected against all species of the parasite in all parts of the world. In addition, treatment schedules have been difficult for busy travelers to adhere to.
60 Degrees Pharmaceuticals is proud to offer an enhanced prophylaxis approach that is effective and easy to follow.
The malaria threat – Prophylaxis
- As of 2020, nearly half of the world’s population was at risk of malaria transmission
- Annually over 241 million cases and more than 627,000 deaths1
- 125 million travelers to endemic regions per annum1,2
- 10,000-plus reported traveler cases of malaria
- Prophylactics utilized by 78% of Europeans and 48% of U.S. citizens when traveling to endemic countries
World Distribution of Malaria
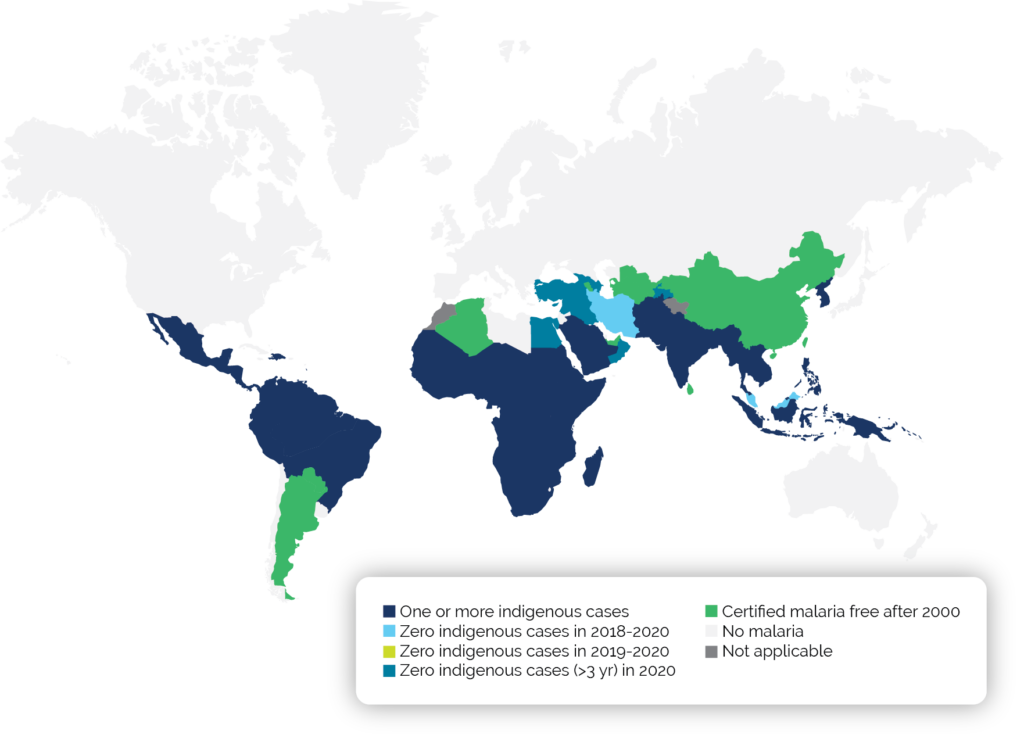
Countries with indigenous cases in 2000 and their status by 2020.2
References 1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About Malaria. Frequently Asked Questions. Page last reviewed: March 22, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/about/faqs.html. Accessed August 15, 2022. 2. World Malaria Report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
Annual deaths from malaria globally
Travelers to malaria endemic regions per annum
Annual dengue infections globally
202-327-5422
1025 Connecticut Ave. NW, Suite 1000, Washington, DC 20036

